Mikromol feature product: Bicalutamide
Featured Product
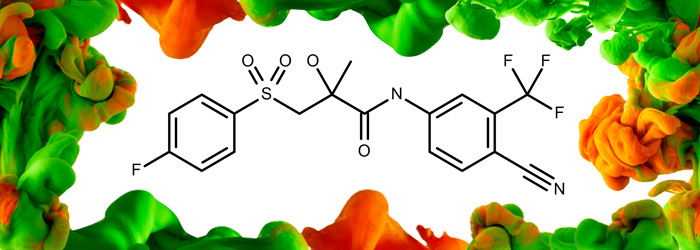
Bicalutamide
API
Product Code: MM0894.00-0250
Introduction
Bicalutamide was first discovered in the 1980s and patented in 1982. It is a type of hormonal drug known as a non-steroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) and is used primarily to treat metastatic prostate cancer, but also prescribed for excessive hair growth or scalp hair loss in women, as well as early puberty and priapism in males. In 1995, AstraZeneca gained approval to market bicalutamide in the UK and US, and it is now on the World Health Organisation’s Model List of Essential Medicines and sold in more than 80 countries.
Mechanism of action
Antiandrogens work by blocking the androgen receptor and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. Bicalutamide competes with androgen to bind to androgen receptors, consequently blocking the action of adrenal and testicular androgens that stimulate the growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue. Blocking the effects of androgens helps stop the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Derived from structural modification of flutamide, bicalutamide was originally synthesised as a bacteriostatic agent in 1967 at Schering Plough Corporation and subsequently found to possess antiandrogenic activity. The "bica-" prefix corresponds to the fact that bicalutamide is a bicyclic compound, while "lutamide" is the standard suffix for NSAAs. Bicalutamide is comprised of a racemic mixture of the (R)-bicalutamide and (S)-bicalutamide enantiomers (these standards are also available in the Mikromol portfolio: MM0894.25-0025 and MM0894.26-0025).
Common synthesis

Product Code | Product Name | Degradation product | |
MM0894.11-0025 | N-[4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-oxirane-2-carboxamide | Impurity | Intermediate |
MM0894.03-0025 | Impurity | | |
MM0894.04-0025 | Impurity | | |
MM0894.25-0025 | API component | | |
MM0894.26-0025 | API component | | |
MM0894.18-0025 | N-[4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-methylprop-2-enamide | Impurity | Intermediate |
MM0894.20-0025 | Impurity | | |
MM0894.08-0025 | (RS)-N-[4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-(3-fluorophenylsulfonyl)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide | Impurity | |
MM0894.01-0025 | N-[4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-fluorophenyl)sulfinyl]-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide | Impurity | |
MM0894.05-0025 | Impurity | Intermediate | |
MM0894.12-0025 | Impurity | Intermediate | |
MM0894.11-0025 | N-[4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-oxirane-2-carboxamide | Impurity | Intermediate |
